We like to cut things in half!
We like to double things!
“Few false ideas have more firmly gripped the minds of so
many intelligent [people] than the one that,
if they just tried, they could invent a [convenient] cipher
that no one could break.”
- David Kahn, in “The Codebreakers”
Discussion question:
What do you think underpins this sentiment?
Would you guess that in theory, a perfect, convenient cipher is a
catch-22?
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Catch-22_(logic)
E.g.,
“If all jobs require experience,
how can one get any experience,
until one gets a job that provides experience?”
document.querySelector('video').playbackRate = 1.2Chapters 22-23
http://inventwithpython.com/cracking/
Read this brief review of crypto-related math:
https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Cryptography/Mathematical_Background
Read Appendix B on Modular arithmetic:
https://github.com/crypto101/crypto101.github.io/raw/master/Crypto101.pdf
Applied uses include generation of:
Keys for asymmetric public-key algorithms (not covered yet, up
next).
A key to kick-start a pseudo-random stream key for symmetric stream
cipher.
Symmetric key for use as a temporary session key.
Creating a digital envelope with as asymmetric keys.
Handshaking in crypto-systems to prevent replay attacks.
Session keys.
https://www.2uo.de/myths-about-urandom/
(a good article)
Uniform distribution:
Frequency of occurrence of each of the numbers should be approximately
the same (in the limit).
Independence:
Implies no one value in the sequence should be able to be inferred from
the others.
Each number should be statistically independent of
other numbers in the sequence.
An opponent should not be able to predict future elements of the
sequence,
on the basis of earlier elements,
event if a partner can, or should.
Cryptographic applications typically make use of algorithmic
techniques for random number generation.
Pseudorandom algorithms are deterministic.
Therefore, they produce sequences of numbers that are not truly
statistically random.
Pseudorandom numbers:
Satisfy statistical randomness tests.
Are possibly predictable (certainly given the seed and the
algorithm).
True random number generator (TRNG):
Uses a non-deterministic (physical) source to produce randomness.
Most operate by measuring unpredictable natural physical
processes,
e.g. radiation, gas discharge, leaky capacitors.
Increasingly provided on modern processors.
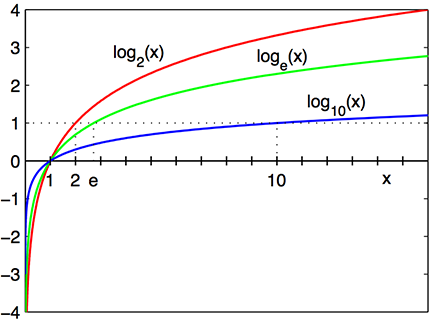
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Logarithm
Subtraction is the inverse of addition.
Division is the inverse of multiplication.
Logarithm is the inverse of exponentiation.
CS often variations of \(\log_2 x\)
directly or indirectly.
Why?

We like to cut things in half!
We like to double things!
Generally:
\(\log_b x = y\)
\(b^y=x\)
\(b^{\log_b x}=x\)
Example:
\(\log_2 64 = 6\)
\(2^6=64\)
\(2^{\log_{2} 64}=64\)
The function:
\(\log_2 x\)
intersects x-axis at 1, and
passes through the points with coordinates (2, 1), (4, 2), and (8, 3),
e.g.,
\(\log_2 8 = 3\)
\(2^3=8\)
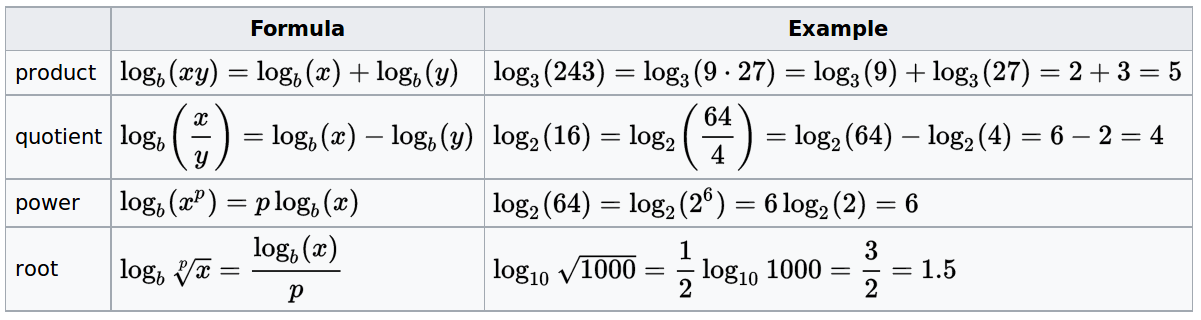
\(\log (nm) = \log n + \log m\)
\(\log (\frac{n}{m}) = \log n - \log
m\)
\(\log(n^r) = r \log n\)
\(\log_a n = \frac{\log_b n}{\log_b
a}\)
(base switch)
+++++++++++++++++++++
Cahoot-07.1
\(n^x \cdot n^y = n^{x+y}\)
\((n \cdot b)^x = n^x \cdot b^x\)
\(n^1 = n\)
\((n^x)^y = n^{x \cdot y}\)
Spend time on this last one!
How can we share a number publicly and produce a secret???
Demo an example in class.
All of the above equivalence statements are also true, mod
p.
In particular, consider the last formula above,
where the below statements are all equivalent:
\((g^a \mod p)^b \mod p =\)
\(g^{ab} \mod p =\)
\(g^{ba} \mod p =\)
\((g^b \mod p)^a \mod p\)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Discrete_logarithm
Log’s equivalent operation for integers alone is the “discrete
logarithm”.
We do this with modular arithmetic.
For example,
\(3^6 \equiv 9 \mod 15\)
\(\log_3 9 \equiv 6 \mod 15\)
Unlike modular inverses,
computing discrete logarithms is generally computationally
hard.
It is similar to integer factorization.
There is no formal proof that computing discrete logarithms is
intrinsically complex.
We just haven’t found any efficient algorithms to do it.
Given the ease going forward,
and the difficulty going “backward”,
we sometimes call this a one way function.
See section and code here:
../../ComputationalThinking/Content/Recursion.html#exponentiation
The efficient algorithm reviewed at that link is often used to generate RSA keys.
We will review:
Greatest common divisor of integers.
Group and group operations.
Euler’s Theorem.
If a and b are integers such that b >
0,
then there are unique integers q and r such
that:
\(a = bq + r\)
where:
\(0 \le r < b\)
For example:
a = 17
b = 5
with q = 3 and r = 2
a = (3 * b) + 2
If a and b are integers,
the linear combination of a and b is a sum of the form ax + by,
where both x and y are integers.
What are some the linear combinations of 9x + 15y?
Among these combinations are:
-6 = 9 * 1 + 15 * (-1)
-3 = 9 * (-2) + 15 * 1
0 = 9 * 0 + 15 * 0
3 = 9 * 2 + 15 * (-1)
-6 = 9 * (-1) + 15 * 1It can be shown that the all linear combinations of 9 and 15
include:
{…, -12, -9, -6, -3, 0, 3, 6, 9, 12, …}
The greatest common divisor (gcd) of two integers a and b, not both
zero,
is the largest of the common divisors of a and b.
For example (note linear combination above):
gcd(9, 15) = 3
The greatest common divisor of the integers a and b, not both
0,
also happens to be the least positive integer that is a linear
combination of a and b.
For example (note linear combination above):
gcd(9, 15) = 3
Basic facts related to GCD and divisibility.
These may aid in understanding some of the proofs to come:
Where:
x | y means that x divides y
The order of this | symbol the opposite of what you might think.
Fact 1:
d | a and d | b implies:
d | (am + bn)
Fact 2:
d | a and d | b implies:
d | gcd(a, b)
Fact 3:
gcd(0, 0) = 0 and
gcd(a, 0) = |a|
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euclidean_algorithm
For any non-negative integer a,
and any positive integer b,
gcd(a, b) = gcd(b, a mod b).
// Pseudocode:
Euclid(a, b)
a and b are non-negative integers
if b = 0 then
return a
else
return Euclid(b, a mod b)https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Extended_Euclidean_algorithm
Suppose:
d = gcd(a, b).
The extended Euclidean algorithm finds the linear combinations of
d,
in terms of a and b.
It is also used to find the modular multiplicative inverse of a
number,
in a group mod n.
The algorithm is often used to generate RSA keys.
// Pseudocode
Extended_Euclid(a, b)
a and b are non-negative integers, and / is floor division
if b = 0 then
return (a, 1, 0)
else
(g', x', y') = Extended_Euclid(b, a mod b)
(g, x, y) = (g', y', x' - (a/b) y')
return (g, x, y)A group G is a set of elements,
together with a binary operation (e.g., +),
such that:
Closure under +:
For every a and b in G,
a + b is a unique element of G.
Associative:
For all a, b, and c in G,
a + (b + c) = (a + b) + c
Identity element:
The set has a unique identity element e,
for every element a of G,
such that, a + e = e + a = a
Inverse:
Every a of G has a unique inverse a-1 in G,
such that, a + a-1 = a-1 + a = e
\(Z^+_n\) = {0, 1, 3, …, n-1}
generally denotes an additive group,
with addition modulo n as the group operator.
Example:
Suppose n = 35
then \(Z^+_{35}\) = {0, 1, 2, …,
34}
Closure examples
If a = 7 and b = 13,
then a + b = 7 + 13 mod 35 = 20
If a = 17 and b = 33,
then a + b = 17 + 33 mod 35 = 15
Associative example
(3 + 11) + 27 % 35 = 6
3 + (11 + 27) % 35 = 6
Identity example
In \(Z^+_{35}\) the additive
identity element is 0
Inverse example
In \(Z^+_{35}\) the
inverse of 17 is 18.
(17 + 18) % 35 = 0
(18 + 17) % 35 = 0
Group under multiplication of the invertible elements of a field,
ring,
or other structure for which one of its operations is referred to as
multiplication.
The multiplicative group of integers modulo n,
is the group under multiplication of the invertible elements Z/nZ
(those numbers lesser than,
n that are relatively prime to n,
with modular multiplicative inverses mod n).
When n is not prime,
there are elements other than zero that are not invertible.
The following generally denotes a multiplicative group,
with multiplication modulo n as the group operator:
\(Z^*_n = \{a| 0< a < n \land \gcd(a,n)
= 1\}\)
The set of positive numbers,
less than n,
which have no shared factors with n.
Example:
Suppose n = 35, then
\(Z^*_{35} = {1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 13,
16, 17, 18, 19, 22, 23, 24, 26, 27, 29, 31, 32, 33, 34}\)
Ask:
How many numbers are there?
Why are some missing?
What does this remind us of?
35 is NOT a prime number,
but n generally could be one…
Closure examples
If a = 8 and b = 13,
then a * b = 8 * 13 mod 35 = 34
If a = 17 and b = 33,
then a * b = 17 * 33 mod 35 = 1
Associative example
(3 * 11) * 27 % 35 = 16
3 * (11 * 27) % 35 = 16
Identity example
In \(Z^*_{35}\) the
identity element is 1
9 * 1 = 9
3 * 1 = 3
Inverse example
In \(Z^*_{35}\) the
inverse of 17 is 33.
(17 * 33) % 35 = 1
(33 * 17) % 35 = 1
Recall:
How to efficiently find the inverse of an element in a large
multiplicative group?
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fermat%27s_little_theorem
If p is a prime number, then for any integer a:
\(a^p \equiv a \pmod p\)
and also:
the number ap - a is an integer multiple of p,
(ap - a is equal to p times something)
For example, if a = 2 with modulus p = 7, then:
27 -2 = 126
27 = 128
128 // 7 = 18 with remainder 2
128 mod 7 = 2
7 × 18 = 126
which is an integer multiple of 7.
If a is not divisible by p,
then it is equivalent to stating that:
\(a^{p-1} \equiv 1 \pmod p\)
and ap-1 - 1 is an integer multiple of p,
(ap-1 - 1 is equal to p times something).
For example, if a = 2 and p = 7,
then 26 = 64,
and 7 × 9 = 64 - 1 = 63,
which is an integer multiple of 7.
Remember our trick with 1 in the multiplicative cipher?
Remember this for RSA!
+++++++++++++++++++++
Cahoot-07.2
“Mathematicians have tried in vain to this day to discover
some order in the sequence of prime numbers,
and we have reason to believe that it is a mystery into which
the human mind will never penetrate.”
- Leonhard Euler, 18th-century mathematician
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leonhard_Euler
Discussion question:
Do you have an intuition on this problem?
Must there be a pattern?
Might the sequence be fundamentally un-predictable?
What kind of computational methods might work to discover such a
sequence?
Mention:
Student explorations into this.
A prime number is an integer greater than 1,
and is divisible only by 1 and itself.
A composite number is an integer greater than
1,
and is not a prime.
If gcd(a, b) = 1,
then two integers a and b are relatively
prime.
For positive real numbers x,
let \(\pi(x)\) be defined as the number
of prime numbers less than or equal to x.
What is this similar to above?
Every integer greater than 1 can be written as a product of
primes,
and if the primes are written in non-decreasing order,
then this product of primes is unique.
There are infinitely many primes,
as demonstrated by Euclid around 300 BC.
No known simple formula separates prime numbers from composite
numbers.
However, the distribution of primes within the natural numbers,
in the large limit, can be statistically modeled.
The probability of a randomly chosen number being prime,
is inversely proportional to its number of digits,
that is, to its logarithm.
The ratio of \(\pi(x)\) to \(x/ln(x)\) tends toward 1,
as x goes to infinity:
\(\lim_{x\rightarrow \infty}
\frac{\pi(x)}{x/\ln x} = 1\)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trial_division
Brute force from the bottom up.
Python:
CryptoMath/trial_div.py
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import sys
from typing import List
def trial_division(n: int) -> List[int]:
"""Return a list of the prime factors for a natural number."""
# Prepare an empty list.
factors: List[int] = []
# The first possible factor.
possible_factor: int = 2
# While n still has remaining factors...
while n > 1:
# The remainder of n divided by f might be zero.
if n % possible_factor == 0:
# If so, it divides n. Add f to the list.
factors.append(possible_factor)
# Divide that factor out of n.
n //= possible_factor
# But if f is not a factor of n,
else:
# Add one to f and try again.
possible_factor += 1
# Prime factors may be repeated: 12 factors to 2, 2, 3.
return factors
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("Example trial division of 17: ", trial_division(17))
print("Example trial division of 257: ", trial_division(257))
print("Example trial division of 16: ", trial_division(16))Haskell:
../../DiscreteMath/Content/Code-HRLMP/HL01GS.hs
module HL01GS where
-- | 2 divides into 4
-- >>> divides 2 4
-- True
-- | 3 does not divide into 4
-- >>> divides 3 4
-- False
divides :: Integer -> Integer -> Bool
divides d n = rem n d == 0
-- | The least divisor of 12 is 2
-- >>> ld 12
-- 2
-- | The least divisor of 15 is 3
-- >>> ld 15
-- 3
ld :: Integer -> Integer
ld n = ldf 2 n
-- | The least divisor, from 3 up, of 64 is 4
-- >>> ldf 3 64
-- 4
ldf :: Integer -> Integer -> Integer
ldf k n
| divides k n = k
| n < k ^ 2 = n
| otherwise = ldf (k + 1) n
-- | 7 is prime
-- >>> prime0 7
-- True
-- | 6 is not prime
-- >>> prime0 6
-- False
prime0 :: Integer -> Bool
prime0 n
| n < 1 = error "not a positive integer"
| n == 1 = False
| otherwise = ld n == n
-- | The minimum of [5, 3, 1, 6] is 1
-- >>> mnmInt [5, 3, 1, 6]
-- 1
mnmInt :: [Int] -> Int
mnmInt [] = error "empty list"
mnmInt [x] = x
mnmInt (x : xs) = min x (mnmInt xs)
-- min is provided in Prelude, min' is home-made.
-- | The minimum of 7 and 5 is 5
-- >>> min 7 5
-- 5
min' :: Int -> Int -> Int
min' x y
| x <= y = x
| otherwise = y
-- | The average of [5, 3, 1, 6] is 1
-- >>> average [5, 3, 1, 6]
-- 15 % 4
average :: [Int] -> Rational
average [] = error "empty list"
average xs = toRational (sum xs) / toRational (length xs)
-- | The sum of [5, 3, 1, 6] is 15
-- >>> sum' [5, 3, 1, 6]
-- 15
sum' :: [Int] -> Int
sum' [] = 0
sum' (x : xs) = x + sum' xs
-- | The length of [5, 3, 1, 6] is 4
-- >>> length [5, 3, 1, 6]
-- 4
length' :: [a] -> Int
length' [] = 0
length' (x : xs) = 1 + length' xs
-- | Pre is a prefix of Prefix
-- >>> prefix "Pre" "Prefix"
-- True
-- | fix is not a prefix of Prefix
-- >>> prefix "fix" "Prefix"
-- False
prefix :: String -> String -> Bool
prefix [] ys = True
prefix (x : xs) [] = False
prefix (x : xs) (y : ys) = (x == y) && prefix xs ys
-- | The prime factors of 66 are [2,3,11]
-- >>> factors 66
-- [2,3,11]
factors :: Integer -> [Integer]
factors n
| n < 1 = error "argument not positive"
| n == 1 = []
| otherwise = p : factors (div n p)
where
p = ld n
-- | The prime factors of 66 are [2,3,11]
-- >>> factors' 66
-- [2,3,11]
-- This is just a version using let instead of where.
factors' :: Integer -> [Integer]
factors' n
| n < 1 = error "argument not positive"
| n == 1 = []
| otherwise =
let p = ld n
in p : factors' (div n p)
-- | This is an infinite generator of primes, so only take 5
-- >>> take 5 primes0
-- [2,3,5,7,11]
primes0 :: [Integer]
primes0 = filter prime0 [2 ..]
-- | This is an improved least divisor function, only checking primes.
-- >>> ldp 15
-- 3
ldp :: Integer -> Integer
ldp n = ldpf primes1 n
-- | This is similar to ldf above, but faster.
-- >>> ldpf [2,3,5,7] 64
-- 2
ldpf :: [Integer] -> Integer -> Integer
ldpf (p : ps) n
| rem n p == 0 = p
| n < p ^ 2 = n
| otherwise = ldpf ps n
-- | This is a faster version of primes0.
-- >>> take 5 primes0
-- [2,3,5,7,11]
primes1 :: [Integer]
primes1 = 2 : filter prime [3 ..]
-- | This is a faster version of prime0
-- >>> prime 7
-- True
prime :: Integer -> Bool
prime n
| n < 1 = error "not a positive integer"
| n == 1 = False
| otherwise = ldp n == n
a = 3
b = 4
-- | f is a function that takes the sum of squares of x and y
-- >>> f 4 5
-- 41
f :: Integer -> Integer -> Integer
f x y = x ^ 2 + y ^ 2
-- | g of 0 is 1
-- >>> g 0
-- 1
-- | g of anything else is a function of x
-- >>> g 5
-- 32
g :: Integer -> Integer
g 0 = 1
g x = 2 * g (x - 1)
-- | h1 of 0 is 0
-- >>> h1 0
-- 0
-- h1 of anything els has a problem. Ask class what it is.
h1 :: Integer -> Integer
h1 0 = 0
h1 x = 2 * h1 x
-- | h2 of 0 is 0
-- >>> h2 0
-- 0
-- h2 of anything else has a problem too.
h2 :: Integer -> Integer
h2 0 = 0
h2 x = h2 (x + 1)https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sieve_of_Eratosthenes
The sieve of Eratosthenes is a simple, ancient algorithm,
for finding all prime numbers up to any given limit.
Mark as composite (i.e., not prime) the multiples of each prime,
starting with the first prime number, 2.
multiples of 2:
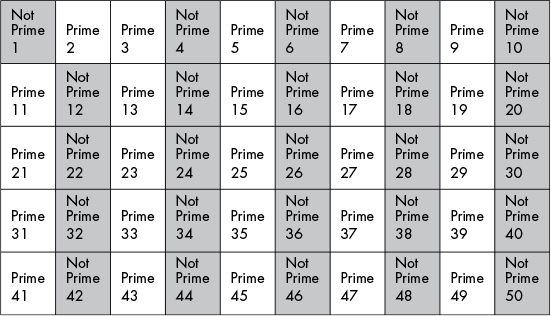
multiples of the next available number (prime 3)
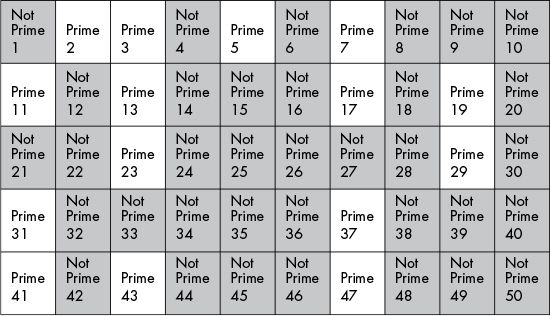
…
Python:
CryptoMath/primeNum.py
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Prime Number Sieve
# https://www.nostarch.com/crackingcodes/ (BSD Licensed)
import math, random
from typing import List
def isPrimeTrialDiv(num: int) -> bool:
# Returns True if num is a prime number, otherwise False.
# Uses the trial division algorithm for testing primality.
# All numbers less than 2 are not prime:
if num < 2:
return False
# Is num divisible by any number up to the square root of num?
for i in range(2, int(math.sqrt(num)) + 1):
if num % i == 0:
return False
return True
def primeSieve(sieveSize: int) -> List[int]:
# Returns a list of prime numbers calculated using
# the Sieve of Eratosthenes algorithm.
sieve = [True] * sieveSize
# Zero and one are not prime numbers.
sieve[0] = False
sieve[1] = False
# Create the sieve:
for i in range(2, int(math.sqrt(sieveSize)) + 1):
pointer = i * 2
while pointer < sieveSize:
sieve[pointer] = False
pointer += i
# Compile the list of primes:
primes = []
for i in range(sieveSize):
if sieve[i] == True:
primes.append(i)
return primes
def rabinMiller(num: int) -> bool:
# Returns True if num is a prime number.
if num % 2 == 0 or num < 2:
# Rabin-Miller doesn't work on even integers.
return False
if num == 3:
return True
s = num - 1
t = 0
while s % 2 == 0:
# Keep halving s until it is odd (and use t
# to count how many times we halve s):
s = s // 2
t += 1
# Try to falsify num's primality 5 times.
for trials in range(5):
a = random.randrange(2, num - 1)
v = pow(a, s, num)
# (This test does not apply if v is 1.)
if v != 1:
i = 0
while v != (num - 1):
if i == t - 1:
return False
else:
i = i + 1
v = (v**2) % num
return True
# Most of the time we can quickly determine if num is not prime
# by dividing by the first few dozen prime numbers. This is quicker
# than rabinMiller(), but does not detect all composites.
LOW_PRIMES = primeSieve(100)
def isPrime(num: int) -> bool:
# Return True if num is a prime number. This function does a quicker
# prime number check before calling rabinMiller().
if num < 2:
# 0, 1, and negative numbers are not prime.
return False
# See if any of the low prime numbers can divide num:
for prime in LOW_PRIMES:
if num == prime:
return True
if num % prime == 0:
return False
# If all else fails, call rabinMiller() to determine if num is a prime:
return rabinMiller(num)
def generateLargePrime(keysize: int = 1024) -> int:
# Return a random prime number that is keysize bits in size:
while True:
num = random.randrange(2 ** (keysize - 1), 2 ** (keysize))
if isPrime(num):
return numHaskell:
../../DiscreteMath/Content/Code-HRLMP/HL03TUOLP.hs
module HL03TUOLP where
evens = [x | x <- [0 ..], even x]
prime :: Integer -> Bool
prime n
| n < 1 = error "not a positive integer"
| n == 1 = False
| otherwise = ldp n == n
where
ldp = ldpf primes
ldpf (p : ps) m
| rem m p == 0 = p
| p ^ 2 > m = m
| otherwise = ldpf ps m
primes = 2 : filter prime [3 ..]
sieve :: [Integer] -> [Integer]
sieve (0 : xs) = sieve xs
sieve (n : xs) = n : sieve (mark xs 1 n)
where
mark :: [Integer] -> Integer -> Integer -> [Integer]
mark (y : ys) k m
| k == m = 0 : mark ys 1 m
| otherwise = y : mark ys (k + 1) m
primes :: [Integer]
primes = sieve [2 ..]
oddsFrom3 :: [Integer]
oddsFrom3 = 3 : map (+ 2) oddsFrom3
mersenne = [(p, 2 ^ p - 1) | p <- primes, prime (2 ^ p - 1)]
notmersenne = [(p, 2 ^ p - 1) | p <- primes, not (prime (2 ^ p - 1))]
pdivisors :: Integer -> [Integer]
pdivisors n = [d | d <- [1 .. (n - 1)], rem n d == 0]
primePairs :: [(Integer, Integer)]
primePairs = pairs primes
where
pairs (x : y : xys)
| x + 2 == y = (x, y) : pairs (y : xys)
| otherwise = pairs (y : xys)
primeTriples :: [(Integer, Integer, Integer)]
primeTriples = triples primes
where
triples (x : y : z : xyzs)
| x + 2 == y && y + 2 == z = (x, y, z) : triples (y : z : xyzs)
| otherwise = triples (y : z : xyzs)../../DiscreteMath/Content/Code-HRLMP/Sol03.hs
module Sol03 where
import HL03TUOLP
-- 3.38
fasterprimes :: [Integer]
fasterprimes = 2 : sieve oddsFrom3
-- 3.39
examples = [take n primes | n <- [0 ..], not (prime (product (take n primes) + 1))]https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euler%27s_totient_function
Background and reminder:
Not every element of a complete residue system, modulo m,
has a modular multiplicative inverse,
for instance, zero never does.
After removing the elements of a complete residue system that are not
relatively prime to m,
what is left is called a reduced residue system,
all of whose elements have modular multiplicative inverses.
The number of elements in a reduced residue system is \(\phi(m)\),
where \(\phi\) is Euler’s totient
function,
i.e., the number of positive integers less than m,
that are relatively prime to m.
Euler’s totient function, \(\phi(n)\),
is the count of the positive integers up to a given integer n,
that are relatively prime to n.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euler%27s_theorem
Let a and n be positive integers and relative primes.
and \(\phi(n)\) is Euler’s totient
function, then:
\(a^{\phi(n)} \equiv 1 \pmod n\)
Further, there is a a special case of the totient.
Suppose we have two primes, p and q,
we take their product, n = p * q,
then is proven true that:
\(\phi(n) = (p-1)(q-1)\)
Suppose
n = 35
a = 17
\(\phi(35) = (5-1)(7-1) = 24\)
\(a^{\phi(n)} \mod n = 17^{\phi(35)} \mod 35
= 1\)
Ask:
This is a generalization of what above function?
Show them side by side.
Such a generalization is a big deal in math.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fermat%27s_little_theorem#Generalizations
Remember our trick with 1 in the multiplicative cipher?
Remember this for RSA!
+++++++++++++++++++++
Cahoot-07.3
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Primality_test
Euler’s theorem forms a foundation for identifying primes:
If a and n are relative prime, and
\(a^{\phi(n)} \mod n = 1\), then:
n is a probably a prime…
Miller-Rabin probabilistic primality test
probably gives you the right answer:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Miller%E2%80%93Rabin_primality_test
If it says not-prime,
then it’s not prime.
If it says prime,
then there is a very, very, very small chance of it being composite.
Haskell implementation:
https://wiki.haskell.org/Prime_numbers
https://rosettacode.org/wiki/Miller%E2%80%93Rabin_primality_test#Haskell
#!/usr/bin/runghc
-- https://programmingpraxis.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/09/primenumbers.pdf
-- https://programmingpraxis.com/programming-with-prime-numbers-source-code-in-haskell/
import Control.Monad (forM_, when)
import Control.Monad.ST
import Data.Array.ST
import Data.Array.Unboxed
import Data.List (sort)
ancientSieve :: Int -> UArray Int Bool
ancientSieve n = runSTUArray $ do
bits <- newArray (2, n) True
forM_ [2 .. n] $ \p -> do
isPrime <- readArray bits p
when isPrime $ do
forM_ [2 * p, 3 * p .. n] $ \i -> do
writeArray bits i False
return bits
ancientPrimes :: Int -> [Int]
ancientPrimes n =
[ p
| (p, True) <-
assocs $ ancientSieve n
]
sieve :: Int -> UArray Int Bool
sieve n = runSTUArray $ do
let m = (n - 1) `div` 2
r = floor . sqrt $ fromIntegral n
bits <- newArray (0, m - 1) True
forM_ [0 .. r `div` 2 - 1] $ \i -> do
isPrime <- readArray bits i
when isPrime $ do
let a = 2 * i * i + 6 * i + 3
b = 2 * i * i + 8 * i + 6
forM_ [a, b .. (m - 1)] $ \j -> do
writeArray bits j False
return bits
primes :: Int -> [Int]
primes n = 2 : [2 * i + 3 | (i, True) <- assocs $ sieve n]
tdPrime :: Int -> Bool
tdPrime n = prime (2 : [3, 5 ..])
where
prime (d : ds)
| n < d * d = True
| n `mod` d == 0 = False
| otherwise = prime ds
tdFactors :: Int -> [Int]
tdFactors n = facts n (2 : [3, 5 ..])
where
facts n (f : fs)
| n < f * f = [n]
| n `mod` f == 0 =
f : facts (n `div` f) (f : fs)
| otherwise = facts n fs
powmod :: Integer -> Integer -> Integer -> Integer
powmod b e m =
let times p q = (p * q) `mod` m
pow b e x
| e == 0 = x
| even e =
pow
(times b b)
(e `div` 2)
x
| otherwise =
pow
(times b b)
(e `div` 2)
(times b x)
in pow b e 1
isSpsp :: Integer -> Integer -> Bool
isSpsp n a =
let getDandS d s =
if even d
then getDandS (d `div` 2) (s + 1)
else (d, s)
spsp (d, s) =
let t = powmod a d n
in if t == 1 then True else doSpsp t s
doSpsp t s
| s == 0 = False
| t == (n - 1) = True
| otherwise = doSpsp ((t * t) `mod` n) (s - 1)
in spsp $ getDandS (n - 1) 0
isPrime :: Integer -> Bool
isPrime n =
let ps =
[ 2,
3,
5,
7,
11,
13,
17,
19,
23,
29,
31,
37,
41,
43,
47,
53,
59,
61,
67,
71,
73,
79,
83,
89,
97
]
in n `elem` ps || all (isSpsp n) ps
rhoFactor :: Integer -> Integer -> Integer
rhoFactor n c =
let f x = (x * x + c) `mod` n
fact t h
| d == 1 = fact t' h'
| d == n = rhoFactor n (c + 1)
| isPrime d = d
| otherwise = rhoFactor d (c + 1)
where
t' = f t
h' = f (f h)
d = gcd (t' - h') n
in fact 2 2
rhoFactors :: Integer -> [Integer]
rhoFactors n =
let facts n
| n == 2 = [2]
| even n = 2 : facts (n `div` 2)
| isPrime n = [n]
| otherwise =
let f = rhoFactor n 1
in f : facts (n `div` f)
in sort $ facts n
main = do
print $ ancientPrimes 100
print $ primes 100
print $ length $ primes 1000000
print $ tdPrime 716151937
print $ tdFactors 8051
print $ powmod 437 13 1741
print $ isSpsp 2047 2
print $ isPrime 600851475143
print $ isPrime 2305843009213693951
print $ rhoFactors 600851475143https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Integer_factorization
Integer factorization is the decomposition of a composite number,
into a product of smaller integers.
If these integers are further restricted to prime numbers,
then the process is called prime factorization.
When the numbers are sufficiently large, no
efficient,
non-quantum integer factorization algorithm is
known.
Related to discrete logarithm, how?
These numbers are used in RSA keys:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Semiprime
Briefly mention:
Memristive and quantum work on this upcoming in the next lecture!
https://www.ntru.org/f/hps98.pdf
For now…